A c# program is a set of statements that are normally executed in an oderly manner when there is no need for any repetitions of certain calculations. However in reality we have a number of situations where we may have to change the order of execution based on certain conditions or repeat certain statements until certain specified conditions are met. This involves a kind of decision making to see whether a particular conditions has occurred or not and then to direct the computer (i.e) the compiler to execute certain statements accordingly.Here we are going to discuss about the various types of conditions that are available in decision making and branching concept.
When a program breaks a sequential flow of execution and jumps to another part of the code , it is called as branching. When that branching is based on certain conditions it is referred to as conditional branching. If the branching takes place without any decision then it is known as unconditional branching.
c# contains the following control or conditional or decision-making statements. They are
- if statement
- switch statement
- conditional operator statement
Decision making with if statements in C#
The if statement is one of the most commonly used decision making statement and it is used to control the flow of execution of statements.It takes the following form:
if(expression)
It allows the computer to evaluate the expression then depending upon the result of the evaluation (i.e) (either true or false) the control is sent to the required block.The program at this point has two paths to follow , one for the true condition and the other for the false condition. some examples are listed below:
- if (bank balance is zero)
borrow money
- if (Room is dark )
put on the lights
The if statements may be implemented in different forms based on the complexity of the conditions to be tested.
- simple if statements
- if..else statements
- nested if..else statements
- else if ladder
Simple if statements in C#
the general form of the simple if statement is as follows:
Syntax
if( boolean-expression )
{
statement - block;
}
statement - x;
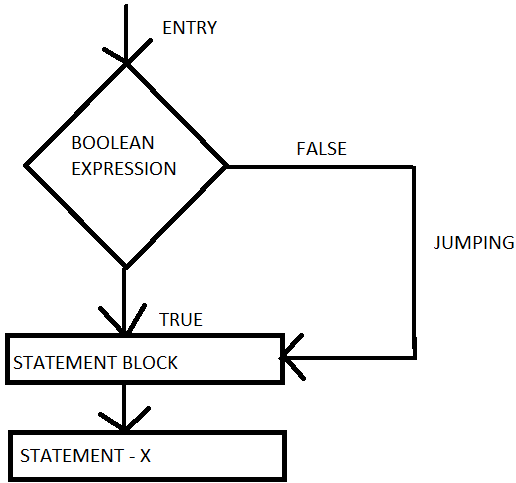
If the boolean expression is the statement – block will be executed or else if the condition is false the statement – x will be executed by just skipping the statement – block . It should be remembered that if the condition is true both the statement – block and statement – x will be executed in sequence. this is illustrated the below flow chart.
consider the following segment of program
if( employee_age >45 )
{
bonus = 2(current_salary)
}
Console.WriteLine(bonus);
the program checks if the following condition ,it checks whether the age of the employee is greater than 45 if so then their bonus is twice of their current salary.
code
using System;
class Simpleif
{
public static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine("enter your age");
int age = Console.ReadLine();
if(age > = 18)
{
Console.WriteLine("you can vote in india");
}
}
}
output
enter your age 24 you can vote in india
in the above program we are asking input from the user if his/her age is greater than or equal to 18 then he can vote but the entered age is less than 18 we have not written any code for that we have written only for the true condition.
if – else statement in C#
The if..else statement is an extension of the simple if statement. The general form is
Syntax
if ( boolean - expression)
{
true - block statements;
}
else
{
false - block statements;
}
statements - x;
if the boolean expression is true then the true – block statements will be executed or else if the boolean expression is false then the false – block statements are executed. In either case, either the true or the false statements are excuted not both. This is illustrated in the below flow chart:
let us consider some examples:
if( brand == tesla)
{
Console.WriteLine(" the quality is extraordinary");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("the quality is mediocre");
}
code:
program to find whether the entered character is an alphabet or not:
using System;
class Alphabet
{
public static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine("enter the letter");
char ch = Console.ReadLine();
if( (ch >='a' && ch <='z') // (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z'))
{
Console.WriteLine("the entered letter is an alphabet");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine(" the entered letter is not an alphabet");
}
}
}
output enter the letter u the entered letter is an alphabet enter the letter 4 the entered letter is not an alphabet'
Nested- if else statements
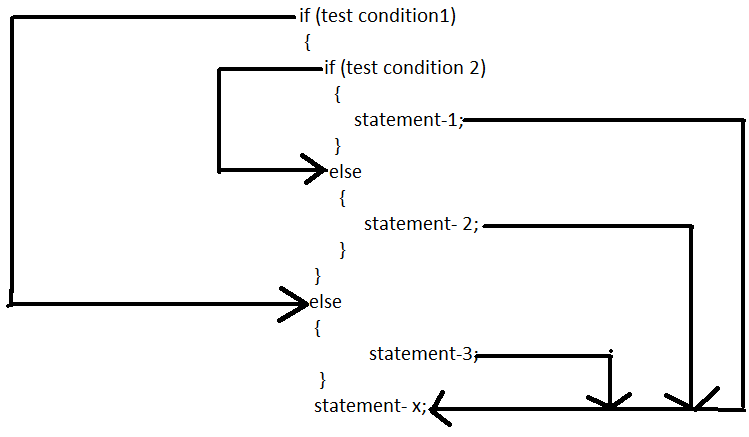
when more than one decisions are involved, we may have to use more than one if..else statement in nested form as follows:the logic of execution is illustrated below.
If the condition-1 is false, the statement – 3 will be executed; otherwise it continues to perform the second test. If condition is true, then statement -1 will be evaluated; otherwise statement- 2 will be evaluated and the control transferred to statement- x.
code:
program to find the biggest of the three numbers
using System;
class Biggest
{
public static void Main()
{
int a= 225, b = 887, c= 220;
Console.WriteLine("largest value is");
if(a>b)
{
if(a>c)
{
Console.WritelLine(a);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine(c);
}
}
else
{
if(c>b)
{
Console.WriteLine(c);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine(b);
}
}
}
}
output
largest value is :887
The else – if ladder
There is another way of putting if’s together when multipath decisions are involved. A multipath decision is a chain of ifs in which the statement associated with each else is an if.let us see the flow of execution.
Let us understand this with a simple code
if(marks > 79)
grade = " honours";
elseif(marks > 59)
grade = "first division" ;
elseif(marks>49)
grade = " second division";
from the above code it is clear that an if is always associated with the else
code
using System;
class Elseif
{
public static void Main()
{
int cp , sp, amount;
Console.WriteLine("enter the cost price");
cp = Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine("enter the selling price");
sp = Console.WriteLine();
if( sp > cp)
{
amount = sp - cp; //profit calculation
Console.WriteLine( "profit is " + amount);
}
elseif( cp > sp)
{
amount = cp - sp ; //loss calculation
Console.WriteLine( "loss is" + amount);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("neither profit nor loss"); //no profit nor loss
}
}
}
output
enter the cost price 200 enter the selling price 250 profit is 50
The switch statement
We have seen that when one of may alternatives has to be selected, we can design a program using the nested if statement but the complexity of the program dramatically increases when the alternatives increases.At time, it can become very tiresome for the programmer thus the c# provides us with the built in multiway decision making statement known as switch. The general form of switch statement is shown below:
Syntax
switch( expression)
{
case value - 1:
block - 1;
break;
case value - 2:
block - 2;
break;
default:
default - block;
break;
}
statement x;
the above set of lines is the general syntax for switch statement.It is explained below
the switch statement is executed in the following order
- the expression is evaluated first.
- the value of the expression is successively compared against the values .If a corresponding case is found whose value matches with the value of the expression then the block of statements that follow are executed.
- the break statement at the end of each block indicates the end of that particular case and causes an exit from the switch statement, transferring the control to the statement x following the switch case.
- the default is an optional case.When present, it will be executed when the value of the expression does not match with any of the mentioned cases. If it is not present and when there is no match the control automatically goes to the statement x.
code
using System;
class Switch
{
public static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine( "select your choice" );
Console.WriteLine("india");
Console.WriteLine("london");
Console.WriteLine("USA");
Console.WriteLine("type your choice");
String name = Console.ReadLine();
switch (name)
{
case "india":
Console.WriteLine(" india: guide 5");
break;
case "london":
Console.WriteLine(" london: guide 6 ");
break;
case "USA":
Console.WriteLine(" usa : guide 7 ");
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("invalid choice");
break;
}
}
}
output
select you choice india london USA type your choice india india : guide 5
This is all about the Decision making and branching in C#. Hope you like the tutorials.