The syllogism is a form of reasoning in which is a conclusion is drawn from two given or assumed prepositions. It is one of the major appearances in the government exams. Each and every candidate must be aware of these type of questions in order to crack the exams with high percentile.
The traditional way or natural way of solving the questions is via Venn diagram method. The following are certain ways on how to draw a Venn diagram as per the need of the questions.
Syllogism Using Venn Diagram
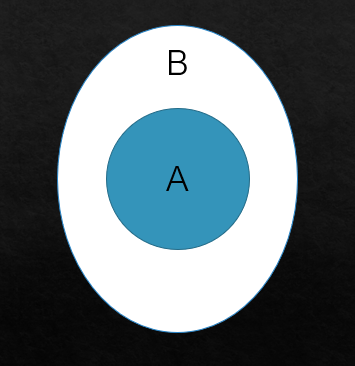
The following Venn diagram is used to represent the sample of Venn diagram of ‘All A are B.’
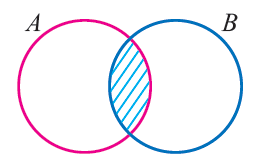
The following Venn diagram is used to represent the sample of Some A are B. Always remember, some means common between some pair.
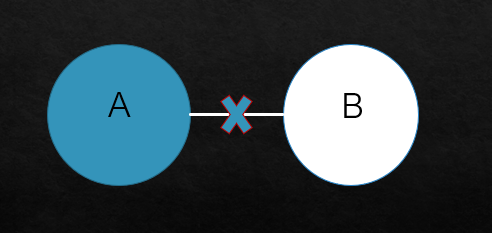
The following is used to represent the sample of ‘No A is B.’
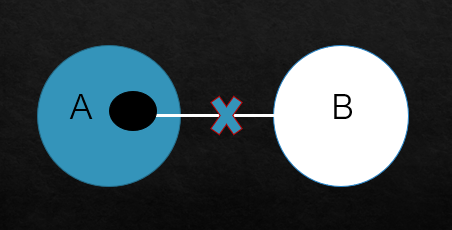
The following Venn diagram is used to represent the sample of ‘Some A are not B’
Let us dive into some problems.
Example ) Statements:
Some A are B.
Some B are C.
All C are D.
Conclusions:
(i) Some D are B
(ii) Some A are D,
Options:
1 Only conclusion (i) follows
2 Only conclusion (ii) follows
3 Both (i) and (ii) follows
4 Either (i) or (ii) follows
5 Neither (i) nor (ii) follows
=> Solution:
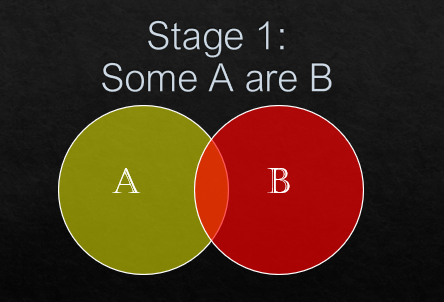
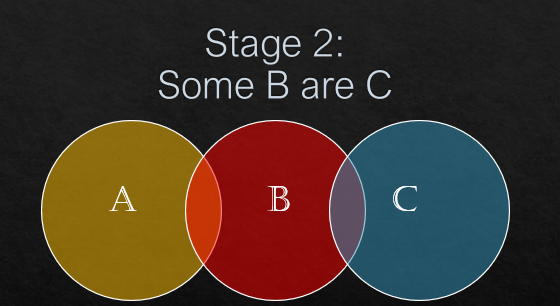
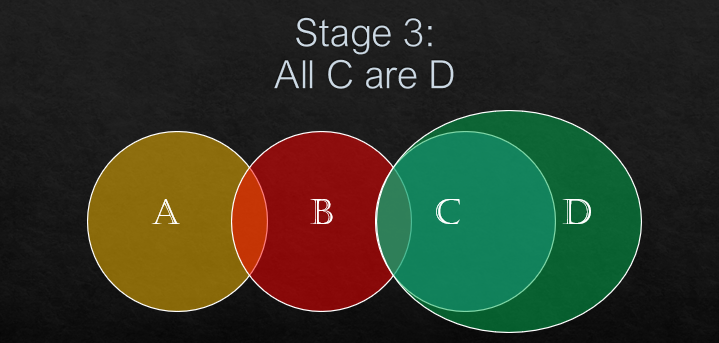
Now, see the conclusion statements.
(i) Some D are B.
Yes, if you can notice all part of C is a part of D. Some part of C is in intersection of some part of B. So, ultimately some part of D is in B. So, Some D are B follows.
(ii) Some A are D.
No, if you can notice that there is no link between the circle of A and circle of D. So, some part of A are mot D.
Answer: 1. Only conclusion 1 follows.
Example ) Statements:
*All L are W
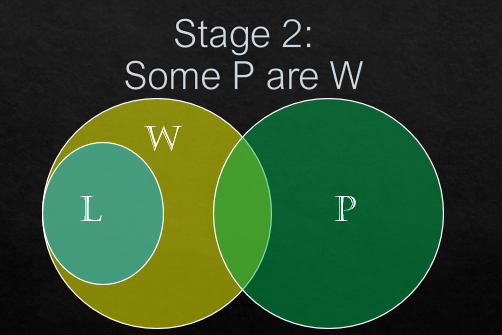
*Some P are W
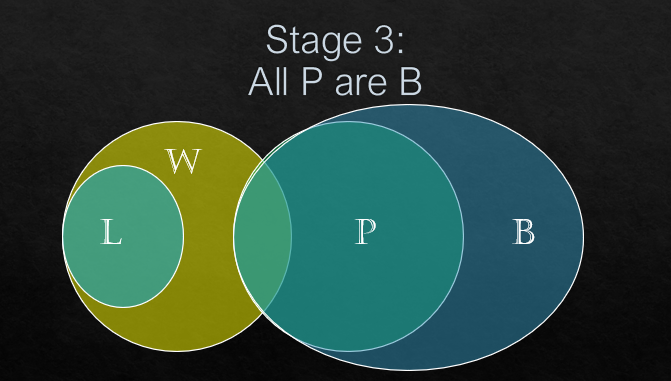
*All P are B
Conclusions:
(i) Some P are W
(ii) Some W are L
Options:
1. Only I follows
2. Only II follows
3. Both I and II follows
4. Either I and II follows
5. Neither I nor II follows
Solutions:
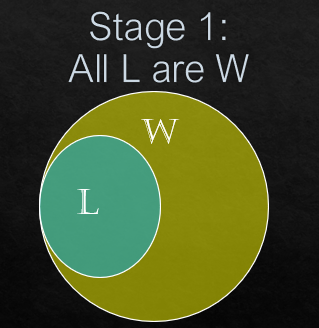
Let us see the conclusions
(i) Some P are W.
Is there any intersection between P circle and W circle? Yes, there is link between P circle and W circle. So, some P are W follows.
(ii) Some W are L.
Is there any intersection between W circle and L circle. Indeed, all L are W. So, some part of W must be L. Even this conclusion follows.
Answer: 3. Both (i) & (ii) follows.
Shortcut trick Venn diagram to solve syllogism question
Let us see some ‘No‘ type questions.
Example ) Statements:
All songs are poems
All poems are rhymes
No rhyme is a paragraph
Some songs are movies
Conclusions:
(i) No song is paragraph
(ii) No poem is paragraph
(iii) Some movies are not paragraph
Let us see which conclusions will work

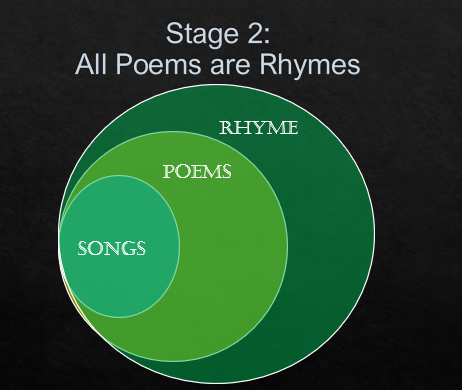
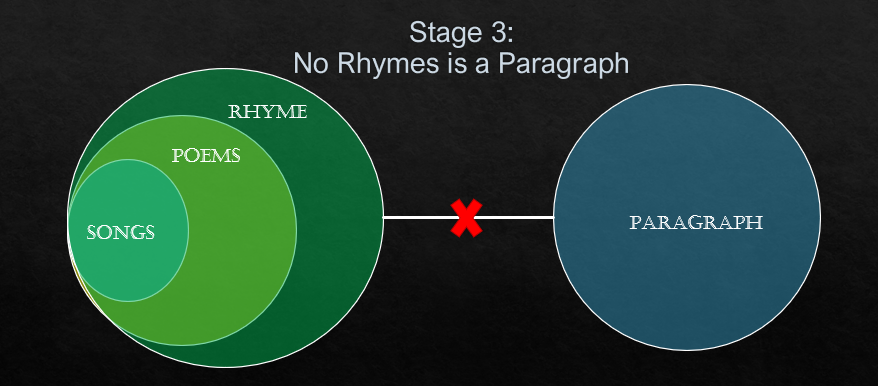
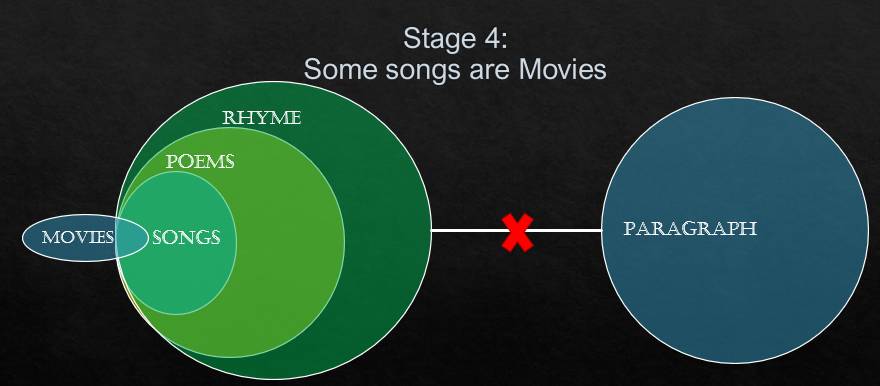
The above Venn diagram is the final picture of Venn diagram.
Let us look into conclusions.
(i) No song is paragraph.
This above-mentioned conclusion follows. As there can be no link between the circles of songs and paragraph
(ii) No poem is paragraph
This above-mentioned conclusion also follows. As you can see there can be no similarity and there is no link between the circles of poems and paragraph.
(iii) Some movies are not paragraph.
This above-mentioned conclusions also follows. Some part of movies is in collaboration with songs and so movies can’t be a part of the paragraph. While this doesn’t rule out the possibility of no movies are not paragraph.
Answer: All conclusion follows
Let us solve another question.
Q. All A is B.
All B is C.
All C is D.
All D is E.
Statements:
(i) All B is A
(ii) Some B is A
(iii) Some A is D
(iv) Some D is A
(v) All D is A
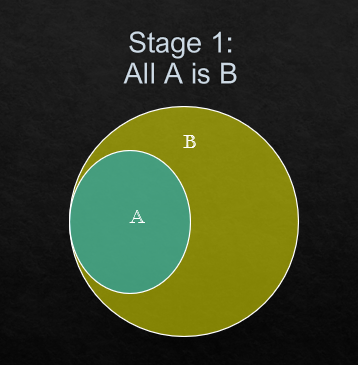
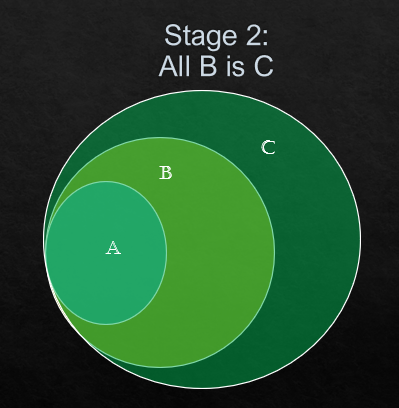
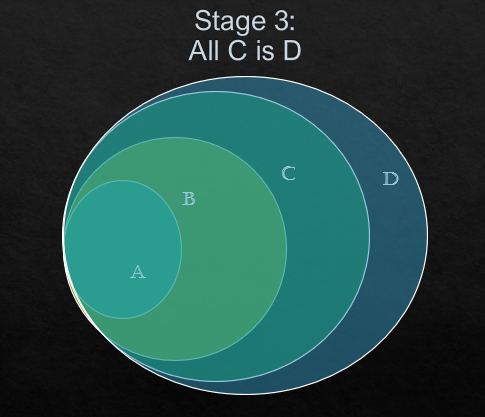
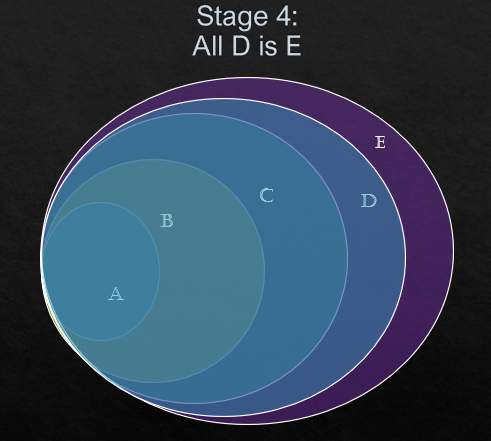
This above Venn diagram is the conclusive diagram and the decision will be taken based on this.
let us see the statements:
(i) All B is A.
See the stage 1. We can notice that some part of B is colliding with A but not the all part of B. So, this is statement is wrong.
(ii) Some B is A.
See the stage 1. We can notice some part of B is colliding with A. So, this statement is right.
(iii) Some A is D.
See the stage 3. All part of A comes under D. So, this proves that Some A is in D.
(iv) Some D is A.
See the stage 3. All part of A comes under D. But, all part of D does not come under A. But some part of D is there in A. So, Some D is A is a right statement
(v) All D is A.
See the stage 3. We can notice that all part of A is under D but all D is not under A. So, this is a wrong statement.
Complex Syllogism Question trick and shortcut
There are questions that can be solved without using a Venn diagram. There require certain tricks. And, Padhle will make u reach there. Let us dive into some tricks now.
1) If the question has two or more than two some statements then, only possibility statements answers will be correct. Definite answers are wrong. Let us walk through definite statements and possibility statements.
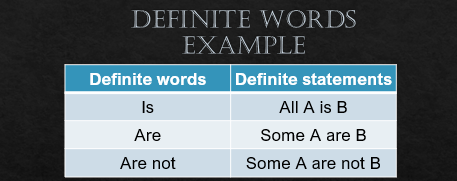
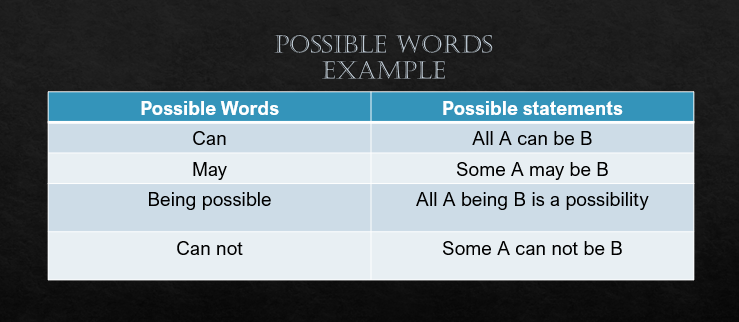
Now, let us walk through an example.
Statements:
1) Some A are B
2) Some B are C
3) Some C are D
Conclusion:
(i) Some A are C
(ii) All A are C
(iii) All D can be B
(iv) All C can be D
Solution:
Let us check the first conclusion
(i) Some A are C
Let us travel from A to C. In order to travel from A to C. Statement 1 and Statement 2 has to be considered. Is there any two or more appearances of some words then, our condition follows. And if we travel from statement 1 from 2, we can spot two some statements.
Our condition says only possibility answers are correct and definite answers are wrong.So, this statement is wrong.
(i) Some A are C is definitive
similarly If we keep on doing this we can find that only statement (iii) and (iv) are correct while the (i) and (ii) are wrong.
(ii) All A are C is also definitive as “are” word used [check the above rule table]
(iii) All D can be B is possibility as “can” word used , so this is correct.
(iv) All C can be D it is also a possibility as statement justify on own – “can” word is used., so this is correct.
2) If there are two or more negative statements then also only possibility answers are correct and definite answers are wrong.
Let us see an example
Statements:
1) No A is B
2) Some B are not C
3) Some C are D
Conclusions:
1) All A are C
2) No A is C
3) All D can be A
4) Some D may not be A
Solutions:
Let us check the first conclusion
(i) All A are C:
Let us travel from A to C. This considers the statements (1 & 2). There are 2 negative words in the statements. So the rule applies, two negative statements means definite answers are wrong and possible answers are correct. So, the first conclusion is wrong as it is definite.
(ii) No A is C:
Let us travel from A to C. This considers the statements (1 & 2). There are 2 negative words in the statements. So the rule applies, two negative statements means definite answers are wrong and possible answers are correct. So, the second conclusion is wrong as it is definite.
(iii) All D can be A:
Let us travel from A to D. This considers the statements (1, 2 & 3). There are 2 negative words in the statements. So the rule applies, two negative statements means definite answers are wrong and possible answers are correct. So, the third conclusion is right as it is a possibility statement.
(iv) Some D may not be A:
Let us travel from A to D. This considers the statements (1, 2 & 3). There are 2 negative words in the statements. So the rule applies, two negative statements means definite answers are wrong and possible answers are correct. So, the fourth conclusion is right as it is a possibility statement.
Answer: Only (iii) & (iv) is correct.
The following tables contains certain conditions which might help you in reducing time while solving the questions of syllogism.
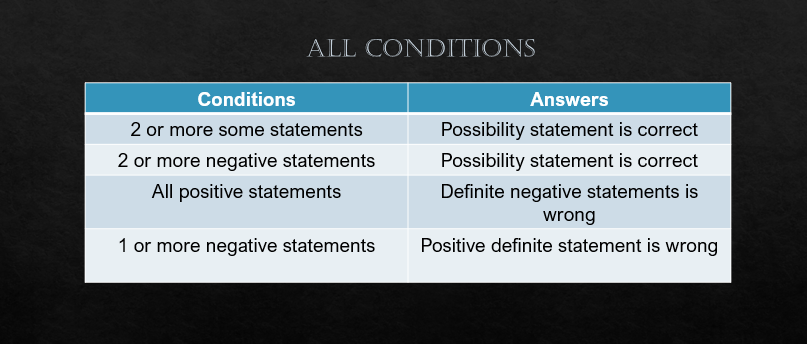
Practice some Syllogism previous year questions
For any queries just leave in the comment section.