In this article – you can revise basics of physics in just 10 minutes. All important concept of each physics chapter is covered here.These amazing physics notes helps to crack any competitive exam , SSC CGl exam , IBPS PO, IBPS clerk, SBI PO , SBI clerk or any government exam.
Table of content
1) Physical quantities
2) Motion , Distance and Displacement
3) Heat Notes
4) Waves notes
5) Light Chapter Notes
6) Magnet and Electricity notes
Physical quantity shortcut and notes
Physical quantity is combination of a number and unit.
Physical quantity is divided into two parts
1) Basic Fundamental Physical quantity – are the quantities which are independent of each other and cannot be expressed by any other basic or derived quantities .
Total 7 basic fundamental physical quantities are –
length , mass , Time, electric current, temperature, luminous intensity and amount of substance.
2) Derived physical quantity – are the physical quantity which can be expressed by two or more basic fundamental quantity , By dividing or multiplying one physical quantity with other physical quantity.
SI units – The international system of units to represent the physical quantities.
Quantities can be of two types
Scalar Quantity – the physical quantity which can be denoted by only magnitude ( numerical value ) . ex – Speed , Electric current
Vector Quantity – The physical quantity which denoted by both magnitude and direction example- velocity , force , acceleration, Momentum, Displacement, Torque etc.
7 Basic Fundamental physical quantities and their SI units
| Basic Quantity | SI Unit/Symbol | Other Units |
|---|---|---|
| Length | metre ( m ) | 1 Kilometre (Km) = 1000 metre 1 metre = 100 centimetre (cm) 1 metre = 1000 millimetre (mm) |
| Mass | Kilogram (Kg) | 1 tonne = 1000 Kg 1 quintal = 100 Kg 1 Kg = 1000 grams (gm) 1 gram = 1000 milligram (mg) |
| Time | Second (s) | 1 minute = 60 seconds 1 hour = 60 minutes 1 day = 24 hours |
| Electric Current | Ampere (A) | 1 Kilo ampere (ka) = 1000 ampere 1 metre = 100 centi ampere (ca) 1 metre = 1000 milli ampere (ma) |
| Temperature | Kelvin (K) | Fahrenheit (F) F = Celsius × (9/5) + 32 Kelvin = Celsius + 273.15 |
| Amount of substance | Mole | |
| Luminous Intensity | Candela |
Important Note – All basic fundamental quantities above are scalar.
Derived Units
| Quantity | Unit |
|---|---|
| Area | Square metre ( m²) |
| Volume | Cubic Metre ( m³ ) |
Motion , Distance and Displacement notes
Motion – A body is said to be in motion when its position is continuously with respect to stationary object.
Two types of Motion
1) Uniform Motion – A body travel equal distance in equal interval of time. Speed of body remain constant throughout the motion.
2) Non Uniform Motion – a body travels unequal distance in equal interval of time , speed of body varies throughout the motion.
Some important term related to Motion
Distance – The actual length of the path traveled by a body.
Speed – It is defined as the distance traveled per unit time.
Formula -> Speed = Distance/Time
SI Unit -> Metre / second [ Metre is SI unit of distance and Second is SI unit of time ]
Average Speed = Total distance / Total Time
Velocity – Speed with direction . Distance traveled by a body per unit time in a given direction.
Uniform Velocity – when body travels in a straight line covering equal distance in equal interval of time.
Average Velocity = [Initial Velocity + final velocity] / 2
Velocity of body can be changed with below 2 ways
1) Change the speed of the body.
2) Change the direction of the body.
Note – Speed has no direction and velocity has direction. All formulas of velocity is same as speed.
Acceleration – Change in velocity of the object with respect to time
Change in velocity = Final Velocity – Initial Velocity
Formula -> Acceleration = change in velocity / Time taken
a = v – u / t
where
a = acceleration
v= Final Velocity
u = Initial velocity
t= time taken for change in velocity
Uniform Acceleration – when velocity of body changes constantly – means equal increment in velocity in equal interval of time. ex – Free falling of a body.
Equations of motion
First Equation of Motion => v = u +at
Second Equation of motion => s = ut + 1/2 at2
Third equation of motion => v2 = u2 + 2as
Where
a = acceleration
v= Final Velocity
u = Initial velocity
t= time taken for change in velocity
s = Distance traveled
Force – an external influence may be push or pull which can change the velocity , shape of an object. SI unit of force is newton ( m/s2).
Newton’s Law of motion
1) Newtons 1st law of Motion – If a body is at rest or moving at a constant speed in a straight line, it will remain at rest or keep moving in a straight line at constant speed unless it is compelled by an external force. Newtons 1st law also known as the law of inertia and Galileo’s law of falling bodies.
2) Newton’s 2nd law of motion – The force acting on the body is directly proportional to the product of the mass of the body and the acceleration produced in the body by the force , the direction of force is direction of acceleration.
Formula -> Force = Mass * acceleration
3) Newton’s 3rd law of motion – Every action has an equal and opposite reaction.Action and reaction act on two different body at same time.
Some applications of newton 3rd law
1) walking
2) Aeroplane and rocket take off
3) Horse pulling a cart
4) Hammering a nail in the wall
Momentum – product of mass of the body and its velocity.
Formula -> Momentum (p) = mass * velocity
Force (f) = change in momentum / time taken
Law of conservation of momentum – Momentum is neither created or destroyed.
Friction – Force which oppose the motion of object in opposite direction.
Note – Sliding friction is smaller than static friction.
Methods to reduce friction
1) By applying oil , lubricant or polishing surfaces..
2) By using roller and wheels.
Pressure – Force acting on an object per unit area.SI unit of pressure is Pascal( Newton/m2).
Formula -> Pressure = Force / Area
Thrust – Force acting perpendicularly on body surface.
Formula -> Thrust= Force / Area
Note – Pressure is inversely proportional to area , so more area -> less pressure or less area -> more pressure.
Archimedes’s Principle – Archimedes’ principle states that the upward buoyant force that is exerted on a body immersed in a fluid, whether fully or partially submerged, is equal to the weight of the fluid that the body displaces.
Applications of Archimedes principle
1) Hydrometers – used for determining the density of liquid.
2) Lactometers – used for determining purity of milk.
Pascal’s law – when there is an increase in pressure at any point in a confined liquid , there is an equal increase in pressure at every other point in the container. ex – Scuba diving applies this law , Hydraulic lift .
Density – mass of the substance per unit volume.
Formula – Density = mass of the substance / Volume of the substance
Gravitation – As per the newton’s law of gravitation , every body in the universe attracts other bodies with some force ( gravitational force ).
Formula –
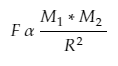
Which means Gravitation Force is directly proportional to product of the mass of two bodies and inversely proportional to the distance between them.
Removing the proportional and adding the gravitational constant.
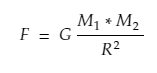
Value of gravitational Constant ( G ) = 6.67 x 10-11 m3 kg-1 s-2
Note –
1) If distance between two bodies is doubled , Gravitational force will become 1/4 .
2) If distance between two bodies is halved , gravitational force will become 4 times.
3) Gravitational force is maximum at the poles of the earth and minimum at the equator of earth.
Acceleration due to gravity – The acceleration which is gained by body because of gravitational force is called its acceleration due to gravity.
Acceleration due to gravity ( g) value on earth is 9.8 m/s2.
Mass – quantity of matter contained in a body. SI unit is Kg . Mass of body remains constant everywhere.
Weight – Weight of the body is the force by which earth attracts a body. SI unit of weight is Newton same as force.
Formula =-> Weight = mass x acceleration due to gravity
Note –
1) weight of a person is different on moon and earth as gravitational force is different on earth and moon.Weight of human being is 6 times on earth than moon.
2) Planets revolve around sun due to gravitational force of the sun.
3) Moon revolve around the earth due to gravitational force of earth.
4) weight is maximum at poles and least at equators as gravity is max at poles and min at equators.
Work – work is done when force produces motion. SI unit of work is Joule.
Formula -> Work ( W) = F * S [where F = Force and S = distance]
Power – the rate of doing work. SI unit of power is watt ( joule/sec ) .
Formula -> Power = Work done / Time taken.
Energy – It is the ability to do work. it is equal to the amount of work .SI unit of work is Joule.
Two types of energy
1) Kinetic energy – Energy of body due to its motion.
Kinetic energy = F * S = 1/2 mv2 [ m = mass , v = velocity]
2) Potential Energy – Energy due to its position or change in shape.
Potential Energy = m * g * h [ m = mass , g = acceleration due to gravity , h = height]
Kinetic energy + Potential Energy =Mechanical Energy
Laws of conservation of energy – Energy can neither be created nor destroyed.It can convert from one form to another.
Escape Velocity -Velocity required to escape from the surface of the planet to overcome its gravitational force like rocket uses escape velocity to launch from earth .
It is 11.16 km/sec at earth surface. It depends on radius and mass of planet . It is different on moon , less escape velocity on moon around 1/5th f earth as moon radius and mass is lesser than earth.
It does not depends on mass of the object.
Heat Notes
Heat is the form of energy. Heat is measured by the temperature. SI Unit of heat is joule. 1 calorie ( unit of heat ) = 4.18 joule.
Temperature is the degrees of hotness. It is measured in degree Celsius , kelvin, Fahrenheit.
Kelvin = Celsius + 273
ex – 0 degree Celsius = 273 kelvin
Mercury Thermometer – Common laboratory thermometer use to measure temperature from -10 to 110 .
Clinical thermometer – used to measure human body temperature . It also consist of mercury.
Note – Normal human body temperature is 37 degree Celsius.
Mercury is used normally in thermometer as it is liquid at room temperature , high coefficient of expansion, high boiling point and does not stick ot glass.
All states of mater expand on heating as the kinetic energy of molecules increases and it starts expanding – gases expands the most , Solid expands the least. Liquid in between solid and gas.
Waves chapter Notes
Periodic Motion – Motion which repeats it self after a fixed interval of time.Example – Motion of a simple pendulum.
Simple Pendulum –
1) Length of Pendulum – The length of the thread from suspension point to the center of bob.
2) Oscillation – One complete two and fro movement of bob.
3) Time Period – Time required to complete one oscillation – it depends only on length of pendulum and acceleration due to gravity.
4) Frequency of oscillation – number of oscillation made in one second. SI unit of frequency is Hertz.
Difference between Electromagnetic waves and Elastic Waves
| Electromagnetic waves | Elastic waves |
|---|---|
| It do not require any medium , can transmitted through vacuum. | It requires medium like solid, liquid or gas for propagation. |
| It caused due to the vibration of the medium particles. | It caused due to varying electric and magnetic field. |
| It has very high frequency , large wavelength and low speed. | It has high very high frequency , very short wavelength and very high speed[3 x 108 m/sec]. |
| It can be transverse wave of longitudinal wave . | It is only transverse waves. |
| Light waves ( radio waves ) | Sound waves |
Transverse waves – waves in which particle of medium vibrates up and down at right angle to the direction of the wave.
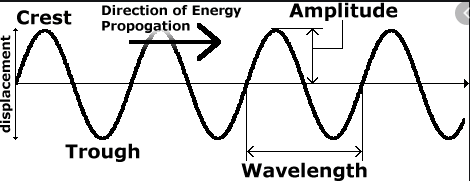
Longitudinal waves – waves in which particle of medium vibrates in back and forth direction.
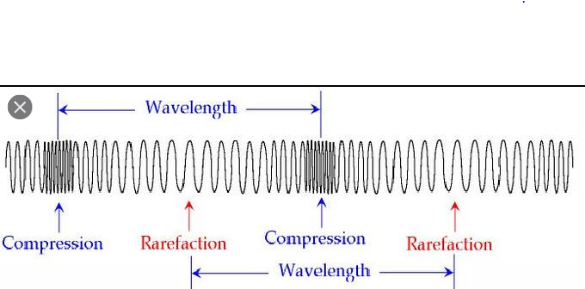
Energy of wave – It is directly proportional to Square of the amplitude.
Intensity of waves – it is defined as power per unit area.
Formula – Intensity = Power / Area
Sound – Sound is the form of energy which makes us hear. Sound cannot travel through vacuum , it need some medium to travel like gas , liquid or solid. SI unit of sound is Decibel.
Sound travel faster in solids and slower in gas.
Echo – The repetition of sound caused by the reflection of sound waves is called an echo.
Ultrasound – The sound having too much high frequency which human cannot hear.
Human Hearing frequency – Human can hear 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.
Sonar – used to measure the depth of sea or locate the object inside sea.
Sunlight – sunlight consits of 3 types of waves –
1) Ultra violet rays – This is invisible to human eyes . It can damage skin by too much exposure.
2) Visible light – It has seven color – VIBGYOR ( violet , Indigo , Blue, Green , yellow , orange , Red)
3) Infrared rays – not visible to human eye eg Tv remotes uses infrared rays.
| Ultra Violet rays | Visible Light | Infra red rays |
| Invisible to human eye | visible to human eye | Invisible to human eye |
| wavelength longer than red color of visible light | It has seven different colors – VIBGYOR Violet has shortest wavelength and Red has highest wavelength. Voilet wavelength – 4 x 10 -7 m Red wavelength – 7 x 10 -7 m | wavelength is shorter than violet rays. |
| Sunlight consist of around 3% to 10 % ultraviolet rays. | Sunlight consist 40 45 %. | Sunlight consist around 50 %. It produces heating effect also. |
Light Chapter Notes
Light – Light travels in a straight line ( rectilinear propagation of light ). Light travels with speed of 3 x 10 8 m/s in vacuum or air. Hence it is maximum in vacuum , then gases , then air and slowest in solids.
Refraction – The deviation of light when it enters from one medium to another.
Laws of refraction
1) Incident ray , Refracted ray and normal lie in the same plane at the point of incidence.
2) Ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence and sine of the angle of refraction is constant ( Snell’s Law ).
Applications of refraction
1) stick or pencil appeared bent in water.
2) coin placed in beaker appeared raised.
3) water tank appear shallower.
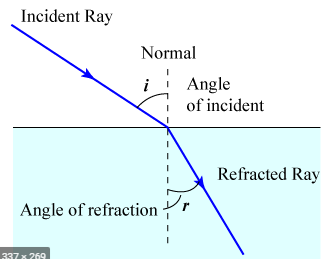
Reflection – when the light falls on the surface of some object and sent back then it is called reflection.
Black object absorbs all the light that’s why we feel warn in black.
Silver metal is the best reflector of light that’s why mirror are painted with silver.
Laws of reflection
1) First law of reflection – Incident ray , Refracted ray and normal lie in the same plane at the point of incidence.
2) Second law of reflection – Angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection.
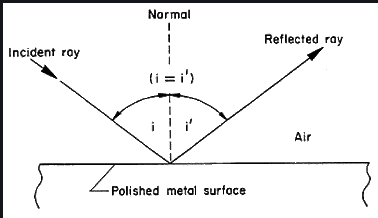
Diffraction – It is the slight bending of light as it passes around the edge or corner of an object.
Total Internal reflection – Complete reflection of a light within a medium when light travels from more optically denser medium to less optically denser medium.It occurs when the angle of incidence must be greater than the critical angle. Application -> Optical fiber [ transmit or absorb light of different colors] .
Note – Mirage in desert is formed by Refraction and total internal reflection.
Concave and Convex mirror difference
| Concave Mirror | Convex Mirror |
|---|---|
| Inner surface is reflecting and polished | outer surface is reflecting and polished. |
| It forms real and inverted image. It can also forms virtual and erect image. | It forms only virtual and erect image. |
| Size of image may be smaller or larger ( enlarged) than object depending upon position of object. | Size of image is always small ( Diminished) than object. |
| Concave mirror used in shaving mirror , by dentist as they form large image. Used in vehicle headlights ,torch to get parallel beams. Used in solar ovens , Microscope , Telescope etc. | Convex mirror used as a rear view mirror in cars and other vehicles. |
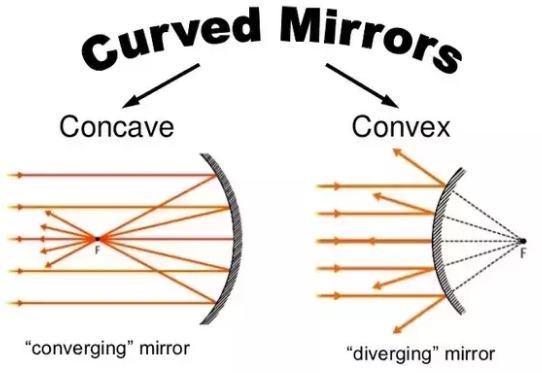
Note – Plane mirror always form same size of virtual image.
Some important concepts of Human Eye
1) Human eye construction and working is similar to photographic camera.
2) Least distance of distinct vision – leas distance from which human eye can see clearly without any pain is 25 cm.
3) human eye can see til infinity.
4) Human eye form real and inverted image.
Magnet and Electricity Notes
Magnet – Magnet attracts the pieces of iron towards itself.
1) Magnetite ( Fe3O4) is the first natural magnet.
2) Magnet point to north south direction when suspended freely. ex- used by sailor to find direction.
3) Like poles of magnet repel each other.
4) Opposite poles attract each other.
5) Heat weakens the magnetism.
6) Used in magnetic compass.
7) Earth act as huge bar magnet.
Electric Current – Flowing of charge through conductor is caled electric current.
Conductors – Material which allow electric current to get passed.
Insulators – Material which do not allow electric current to get passed.
Two types of charge
1) Positively charged body – when the body has deficiency of electrons.
2) Negatively charged body – when the body has excess of electrons.
Note
1) Electric current flows from negatively charged body to positively charged body.
2) Electric cell converts chemical energy to electrical energy.
Photoelectric Effect – When light falls on a metal , electrons can be ejected from the surface of the metals. It is also known as photo emission, and the electrons that are ejected from the metal are called photo electrons.
Note – Electric current always flow on outer surface of conductors .
Electromagnetism – study of electric current and magnet. It is founded by Andre Marie Ampere.
1) Electromagnet – Iron coil or iron bar which acts like a magnet when electric current flows though it.
2) Used in electric appliances like bell , fan etc
3) Faraday’s Experiment – when a magnetic field is changed near a conductor , a current produced in it.
4) Electromagnetic induction – when change in magnetic field within a closed coil produce electric current in coil. This current is also called induced current.
Some important Instrument and its uses
| Instrument | Uses |
|---|---|
| Anemometer | measure power and velocity of wind. |
| Barometer | measure atmospheric pressure. |
| Galvanometer | measure sharpness of electric current. |
| Hydrometer | measure relative density of liquid |
| Hygrometer | measure humidity |
| Pyrometer | measure the temperature of distant objects |
| Psychrometer | measure humidity |
| Thermistor | uses sensors to help regulate cold and heat. |
| Thermocouple | sensor used to measure temperature |
Practice some physics question that frequently asked in examination. For any queries mention in comments and give feedback.