Collection of all important shortcut and concepts of chemistry – General science for the government exam preparation – SSC CGL , Bank PO , Bank Clerk.
Table of content
1) Molecules and Elements Notes
2) Metals and Non Metals Notes
3) Chemical Equilibrium Notes
4) Acids and Base notes
Molecules and Elements
All elements are divided in 3 categories –
1) Metals ( described below in detail)
2) Non – Metals ( described below in detail)
3) Mettaloids – have properties of both metals and non metals.
Mixtures
1) Homogeneous mixture – it is the mixture of two or more substances which are completely mixed with each other and through out it is uniform ex- sugar solution , alloys.
Types of Homogeneous mixture –
Solutions – It is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances which dissolve completely. The solution is uniform through out. Size of particle is less than 1 nm or 10-9 m. example- sugar solution.
2) Heterogeneous mixture – in which substance do not mix and remains separate ex – sugar and salt mixture.
Types of heterogeneous mixture –
Suspensions – It is a heterogeneous mixture in which particles do not dissolve in the solutions and spread through out the solution.Size of particle is more than 100 nm eg – muddy water
Colloids : It appears to be homogeneous but it is heterogeneous. The particles are bigger than solution and smaller than suspensions like foams (shaving cream) , gels (gelatin, jelly), emulsions ( lotion), aerosols (fog, insecticide spray, smoke) and sols (shampoo, gemstones).
Different types of changes in matters
1) Physical change – No new substance is formed , only appearance changes. Only state changes example boiling of water [ liquid change to gas ]
2) Chemical Change – New thing is formed in chemical changes. It is permanent change eg rusting of iron [iron oxide generates]
Methods of separation of solid and liquid solution :-
1) Filtration – eg sand water solution can be separated by filter paper.
2) Centrifugation – solution is rotated at a very high speed to separate it out.
3)Evaporation
4) Crystallization – Solid separates out from liquid on cooling,purify solid from impurities eg – over the time sugar molecules starts crystallize over the time from honey solution.
5) Chromatography
6) Distillation – process to heat liquid to make vapour and then cool vapour to get pure liquid eg salt solution from sea use distillation process to separate salt from water.
Laws of chemical reactions :
Law of conservation of mass – mass can neither be created nor be destroyed.
Law of constant proportion – all samples of that compound will be made up of the same elements in the same proportion or ratio.
Dalton’s Atomic Theory
1) All matter made up of small particles called atoms.
2) Atoms cannot be created or destroyed during reaction.
3) Atoms of a given element are identical in mass and chemical properties.
4) Atoms of different elements are different in mass and chemical properties.
5) During chemical reaction , atoms are rearranged or separated to form different elements.
Atoms – is the smallest particle of an element eg – Hydrogen(H)
Atomic Mass of an element = Mass of one atom of element/1/12th part of mass of one atom of carbon.
Gram Atomic Mass – The atomic mass of an element expressed in grams is called gram atomic mass.
example –
Atomic mass of Nitrogen is 14 , its gram atomic mass is 14 gm.
Molecule – is group of two or more atoms. It is smallest particle of a compound eg – Oxygen (O2).
Atomicity – is a number equal to total number of atoms in a molecule.
Compound – two or more molecules combined to form a compound eg – Water (H2O)
Molecular Mass = Mass of one molecule of substance / 1/12 mass of one atom of 12C .
Mole concept
1 mole of atoms = 6.022×1023 atoms
1 mole of molecule= 6.022×1023 molecule
1 mole of any substance= 6.022×1023 unit of that substance
6.022×1023 – this is Avogadro number
Structure of Atom
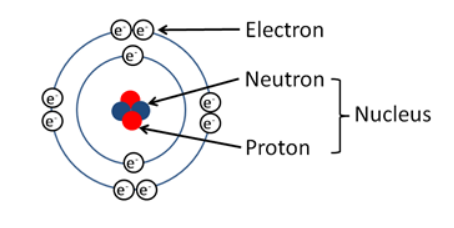
- Atom is consist of 3 particles – electron , Proton , Neutron.
- Neutrons and protons are present inside nucleus
- Outermost regions contains electrons.
- Protons and neutrons have same mass = 1.67 × 10-24 grams.
- Electron is negatively charged and founded JJ thomson in 1987.
- Neutrons has no charge – it is neutral and founded by Chadwick in 1932 and mass = 9 × 10−28 gm = 1/1840 of mass of H atom.
- Protons are positively charged and founded by E. Goldstein.
- Electrons and Protons have charge of 1.6 × 10−19 coulomb.
- Proton and Neutrons are also called nucleons.Mass of atom is inside nucleus.
Note – Hydrogen atom (H) contains only one proton, one electron, and no neutrons.
Electrons are present in number of outer shells K (n=1) , L(n=2) , M(n=3) , N(n=4) and so on.
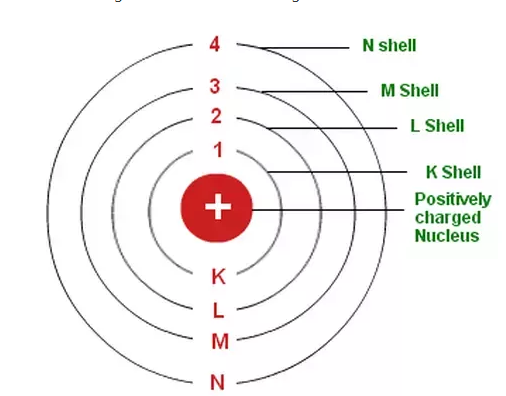
Number of electron in a shell = 2(n2) where n is number of shell ex – for L , n=2 so it can hold 2(22) = 8 electrons.
Atomic Number = number of protons inside an atom.
Mass number = number of protons+ number of neutrons.
For example – calcium has atomic number =20 , Mass number = 40 , so it has 20 protons = atomic number , and 20 electrons ( 20 Protons + 20 Electrons = 40 mass number ).
valence electrons – number of electrons present in outermost shell of an atom that take participate in reactions.
Calcium has 20 electrons so its electrons arrangement in shells is 2,8,8,2 – so its valence electrons is 2.
Valency – the number of loosing or gaining electron to become stable which ever is minimum is called valency.
Inert Elements – The valency of elements is zero and they are stable elements and hence non reactive elements example – Helium, Neon, Argon, Krypton, Xenon & Radon are nonreactive elements.
Isotopes – atoms having same atomic number and different mass number example 11H, 21H, 31H.
Isobars – atoms having same mass number and different atomic number example – 40S, 40Cl, 40Ar.
Isotones – atoms having same number of neutrons.
Isosters – Molecule and ions having same number of atoms and electrons.
Radioactivity – emission of particles due to spontaneous nuclear reaction of a particular element.
Radio activity emits 3 types of particles –
| Alpha particle (α) | fast moving positive charge helium atoms less penetration power |
| Beta particle (β) | fast moving electrons – negatively charged. More penetration than alpha rays. |
| Gamma rays (γ) | are the most energetic form of electromagnetic radiation. It has very short wavelength of less than one-tenth of a nano meter. has greatest penetrating power. |
Nuclear Fusion – joins two light elements forming a heavier element and release energy example – sun and all stars uses the fusion to produce energy.
Nuclear fission– splits heavy element into small particles and release lot of energy.y
Controlled nuclear fission – used for commercial purpose – producing electricity.
Uncontrolled nuclear fission – used in atom bombs – First atom bomb dropped in hiroshima on 6th Aug 1945.
Radium( discovered by Marie Curie and Pierre Curie) and plutonium -239( used in atom bomb) ,Uranium are radio active element used in nuclear fission reactions.
X-rays – rays are electro-magnetic radiation which have short wave length , used for medical diagnoses , tungsten used to produce x-rays.
Important Chemical and their Usage
| Chemical | Uses |
|---|---|
| Nitrous Oxide [N₂O] | called Laughing Gas , Used by dentist for pain relief. |
| Potassium Nitrate [KNO₃] | Used in gun powder , Fire cracker Industry |
| Biogas | used for cooking , Mixture of Methane & carbon dioxide. |
| Sodium Chloride [NACL] | Common Salt – used in cooking food |
| Sodium Hydroxide [NAOH] | Used for making Soap and Detergent. |
| Sodium Carbonate [Na₂CO₃] | Washing soda – used for washing clothes |
| Calcium Sulphate [ CaSO4] | POP(Plaster of Paris) – Used in Home for decoration , used for plaster in hospitals |
| Sodium Bicarbonate [NaHCO₃] | Baking Soda – used as antacid for indigestion or acidity problem |
| Calcium Hypochlorite [Ca(ClO)2] | used in textile industry |
| Magnesium Hydroxide [Mg(OH)₂] | Milk of magnesia – used as an antacid to relieve indigestion, sour stomach. |
| Calcium Oxide [CaO] | Quick Lime – used for medicinal purposes and insecticides , Paper industry , IronProduction. |
| Calcium Hydroxide [Ca(OH)₂] | Slaked Lime – used to make lime water |
| Acetic Acid [CH3COOH] | used in Vinegar. |
| Formic Acid [CH₂O₂] | Ant Bites release this. |
| Citric Acid | Present in lemon and citrus food. |
Change of States – Solid , Liquid and Gas notes
| Process | State Conversion |
|---|---|
| Condensation | Gas to Liquid |
| Deposition | Gas to Solid |
| Vaporization | Liquid to Gas [Water Evaporation point -> 100 Celsius or 373.15 K or 212 F ] Once Water starts boiling its temp remains constant |
| Freezing | Liquid to Solid [Water Freezing point -> 0 Celsius or 273.15 K or 32 F ] |
| Sublimation | Solid to Gas |
| Melting [Fusion] | Solid to Liquid [Water Melting point -> 0 Celsius or 273 K or 32 F ] |
| Super Cooling | Cooling of a liquid below freezing point without changing to solid eg- Glass |
| Diffusion | Movement of particles in surroundings. Diffusion is maximum in gases , then gas and least in solids. Diffusion increases with the increase in temperature . |
Metals and Non Metals Notes
Important Concepts of Iron
- 3 different types of Iron – Pig iron , Cast iron and Wrought iron [purest form of iron].
- Alnico is used for making magnets.
- Casting iron used in daily routines.
- Corrosion of Iron is called rusting.
- Rusting of Iron needs air , moisture or water to get corrode.
- Rusting of Iron increases weight.
- Iron rust in salty water more easily.
- Iron cannot rust in dry air or pure water.
- 3 different types if iron exist – Pig Iron ( impure) , Cast iron , Wrouhgt iron ( Purest iron).
Important Properties of Metals
Ductility – Allows the Metals to be hammered thin or stretched into wire without breaking – Gold is most ductile metal.
Malleability – Allows the Metals to be hammered to thin sheets.Gold is most malleable
Corrosion – it is degradation of metal by air , moisture or water or any other chemical.
Hard – Metals are generally hard except sodium and potassium, we can cut it by knife.
Solid – Metals are solid at room temperature – except Mercury (Hg) – liquid at room temp.
Boiling and melting point – Metals have high melting and boiling point. Mercury(Hg) has lowest melting and boiling point. Tungsten has highest melting and boiling point.
Heat and Electricity – Metals are good conductor of heat and electricity. Silver – Best conductor of heat and electricity and Lead(Pb) – poorest conductor of electricity.
Density – Metals has high density generally. Lithium has lowest density(Light) and Osmium has highest density(Heavy).
Sonorous – Metals produce sounds on hitting.
Lustrous – Meats are generally shiny in nature.
Reactions – Metals are reactive in nature . They can react with water , air , acids and other Solutions.Gold is most reactive and Potassium is least reactive.
Important Properties of Non Metals
Non Ductility – Non metals are non ductile.
Non Malleability – Non metals are non malleable.
Poor Heat and Electricity – Non metals are do not conduct heat and electricity. Carbon is only non metal good conductor of electricity and heat.
Low Boiling and melting point – Non Metals have low melting and boiling point. except graphite has highest melting point in non metals.
Non Lustrous – non metals are not shiny except Iodine which is shiny.
Non Sonorous – Non metals do not produce sounds on hitting.
Reactions – Non metals do not react with water and acids.
Note –
1) Oxygen is most abundant element in earth crust and Aluminium is most abundant metal in earth crust.
2) Acid rain is caused by reaction of sulphur dioxide and nitrogen with air.
3) Bauxite is the ore of aluminium.
4) Galvanization – the process of applying a zinc coating to steel or iron, to prevent rusting.
Minerals – They are combination of one or more element which occurs naturally in earth crust ex – granite.
Ores – The material(rock) or mineral from which pure metals can be extracted eg rocks.
Alloys – mixture of two or more metals to improve metal properties.
Important points to remember –
– Iron get corrodes due to component making of iron oxide[Red brown color ]
– Copper get corrodes due to deposition of copper carbonate and copper hydroxide [green layer ]
– Silver get corrodes due to deposition of silver sulphide layer [ black color] in presence of hydrogen sulphide. silver corrosion called tarnish.
– German Silver is the alloy of copper not silver.
– Alloy of mercury is called amalgam.
– Diamond is hardest known element in world and purest form of carbon.
Coal is 4 different types
| Peat | 50-60 % carbon |
| Lignite | 60-70 % carbon |
| Bituminous | 75-80% carbon, Black color , used as domesctic fuel. |
| Anthracite | 75-90% carbon , Purest form of coal |
Chemical Equilibrium Notes
Types of Reactions
1) Exothermic Reactions – that release energy in form of heat or light.
2) Endothermic Reactions – that absorbs heat during reaction.
3) Photo chemical reactions – that takes place in presence of light.
4) Oxidation Reaction – addition of oxygen or removal of hydrogen.
5) Reduction reaction – addition of hydrogen and removal of oxygen.
6) Oxidizing agent – substance which remove oxygen and give hydrogen.
7) Combining oxidation and reduction is called redox.
Electrolytes Some important terms –
Electrolyte – a substance which conduct electricity when dissolve in water and dissociates into ions.
Two types of electrolyte –
1) Strong Electrolyte- that completely ionize in dilute solutions eg – Sodium Chloride ( NaCl) is very strong electrolyte.
2) Weak Electrolyte – That does not ionize completely in solution.
Non Electrolytes – A substance which do not dissociates in ions in solution and poor conductor of electricity in water.
Ostwald Dilution Law – Degree of dissociation of weak electrolyte is directly proportional to square root of dilution. Not applicable for strong electrolytes.
Acids and Base Important concepts and notes
Acids – which donate protons(Hydrogen ions) and accept electrons.
1) It is sour in taste
2) change blue litmus paper to red.
3) Methyl orange change to red in acid.
4) Phenolphtholein remain color less in acid
Base – which donate electrons and accept protons.
1) It is bitter in taste
2) change red litmus paper to blue.
3) Methyl orange change to yellow in base.
4) Phenolphtholein change to pink in base
Note – Litmus paper is used to test whether a substance is acid or base and to determine pHof the substance.
Acid base reaction –> Acid + Base = Salt + water
pH important notes
pH – is a measure of hydrogen ion concentration, it checks whether solution is acidic , base or neutral. pH scale has range of 0 – 14.pH has no unit it is just a number.
pH – 0 to less than 7 -> Acidic [0 is most acidic]
pH – 7 is neutral(neither acidic nor alkali or basic) – pure water has 7 pH.
pH – more than 7 and till 14 is basic [ 14 is most alkaline or strong base]
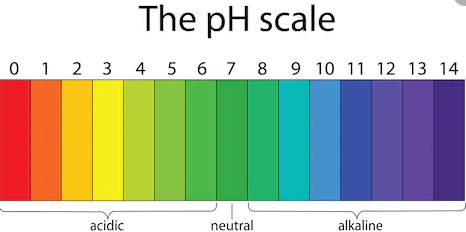
Note – pH of human blood is 7.35 – 7.45 , so it slightly basic or alkali.
Practice chemistry general science question
Hope you enjoyed this article and helps you for your exam preparation – SSC CGL chemistry notes.